At a compound annual growth rate of 22.3%, the size of the worldwide Virtual Router market is projected to reach US$ 614.6 Million in 2027.
.jpg)
A virtual router may be classified as a software-based routing structure, that allow the host devices to work as a traditional hardware router over a local area network. It allows network paths to be segmented for multiple devices when it shares an internet connection. This type of setting also helps organizations in segregating traffic at the same time increasing network security by completely eliminating the need for authentication and encryption. Various functions such as overlapping of IP addresses, network functions virtualization (NFV), traffic routing can also be achieved with a virtual router. The market is expected to be driven by the increasing demand for NFV and software-defined anything networking solutions by the enterprises. In addition to this, more and more telecom and network providers with changing network flexibility in mind are readying up for virtual routers and the benefits it will pass onto them. The inefficiency of the legacy hardware first infrastructure with changing network flexibility is also expected to drive the demand for virtual routers. For enterprises, the use of virtual routers also translates into cost savings as dedicated hardware is not required for routing purposes. With such factors promoting the market growth, there are some that may hinder the market’s growth too. Factor such as virtual routers’ inability to handle heavy duty core IP functions is expected to restrain the market growth. Demand for virtual networking solutions is expected to generated opportunities in the years to come.
Virtual Router Market Scope
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2022 |
| Historic Data | 2017-2018 |
| Forecast Period | 2022-2027 |
| Study Period | 2017-2027 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2027 | US$ 614.6 Million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 22.3 % during 2017-2027 |
| Segment Covered | By Component, by End User, Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South America |
| Key Players Profiled | 6WIND, Allied Telesis Inc., Arista Networks Inc., Check Point Software Technologies Ltd., Cisco Systems Inc., Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd., International Business Machines Corporation, Juniper Networks Inc., Nokia Corporation, Palo Alto Networks Inc. and ZTE Corporation. |
Key Segments of the Global Virtual Router Market
Component Overview
- Software
- On-Premise
- Cloud
- Services
- Consulting
- Integration & Implementation
- Maintenance & Operations
End-User Overview
- Telecom Providers
- Cloud Providers
- Enterprises
Regional Overview
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- UK
- Germany
- France
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Middle East and Africa
- UAE
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East and Africa
- South America
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
Reasons for the study
- The purpose of the study is to give an exhaustive outlook of the global virtual router market. Benchmark yourself against the rest of the market.
- Ensure you remain competitive as innovations by existing key players to boost the market.
What does the report include?
- The study on the global virtual router market includes qualitative factors such as drivers, restraints, and opportunities
- The study covers the competitive landscape of existing/prospective players in the virtual router industry and their strategic initiatives for the product development
- The study covers a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the market segmented based on component, and end-user. Moreover, the study provides similar information for the key geographies.
- Actual market sizes and forecasts have been provided for all the above-mentioned segments.
Who should buy this report?
- This study is suitable for industry participants and stakeholders in the global virtual router market. The report will benefit: Every stakeholder involved in the virtual router market.
- Managers within the virtual router industry looking to publish recent and forecasted statistics about the global virtual router market.
- Government organizations, regulatory authorities, policymakers, and organizations looking for investments in trends of global virtual router market.
- Analysts, researchers, educators, strategy managers, and academic institutions looking for insights into the market to determine future strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) :
The numerous perceived benefits of virtual router platform to an enterprise is expected to drive the market. In times of financial instability, the organizations are focusing on staying afloat by cutting expenses either by improving operational efficiency or retrenchments. Virtual router platform can offer these benefits as no hardware needs to be installed and companies can save money on that. The North America region is anticipated to hold a large chunk of the total market throughout the forecast period owing to the presence of key industry players. The demand for virtual networking solutions could open avenues of opportunities to the vendors. Regional expansion along with collaborations with other virtual router providers are some strategies adopted by key players to strengthen their position in the market.
Component Segment
On the basis of the component, the market is bifurcated into software and services. Solutions are further divided into on-premise, and cloud. Services are further classified into consulting, integration & implementation, and maintenance & operations. The solution sub-segment is expected to hold the major share of the market throughout the forecast period. These include the core products which are software and that provide routing capabilities along with saving on operational costs to the enterprises. The flexibility that these provide is the chief reason for their market share and expected growth in the future.
End-User Segment
Based on end-user, the market is divided into telecom providers, cloud providers, and enterprises. Amongst the said, telecom providers are expected to garner the largest share of the market. This is owing the benefits such as delivering flexible routing functionalities telecom providers receive when the opt for virtual routers. Their central role in communication infrastructure is also expected to help them grow at a considerable growth rate in the years to come.
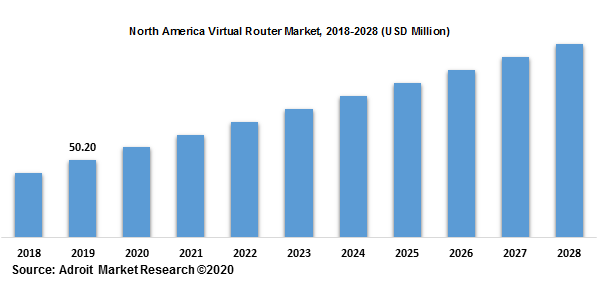
The North American region is anticipated to hold the largest market size in the global virtual router market. North America which is followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific region is expected to hold more than 40% of the total market in 2020. This growth can be attributed to the presence of key industry players that has resulted in greater product development and feature enhancement which in turn is likely to aid the market growth. The increasing focus on networking domain in the region is yet another reason for the high market share of North America. The US is likely to be the largest market in the region with high absorption of virtual router solutions
The major players of the global virtual router market are IBM, Nokia Corporation, Cisco Systems, Brocade Communication Systems, Huawei, Juniper Networks, Net gear Inc., ASUSTek Computer, Edimax Technology, Belkin International, Xiaomi, and D-Link Corporation. These vendors have adopted various traditional and non-traditional growth strategies to enhance their market share including new product launches, partnerships and collaborations, and mergers and acquisitions.

