Fuel Ethanol Market Analysis and Insights:
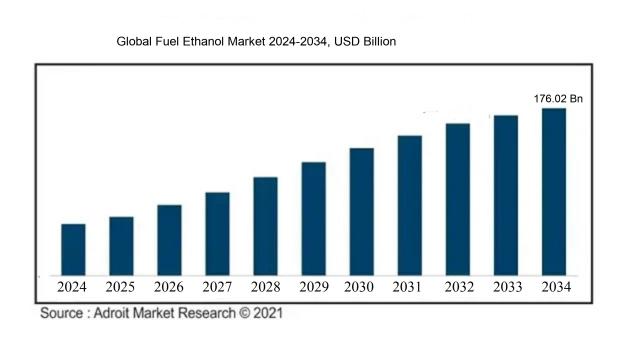
A compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.10% is predicted for the worldwide fuel ethanol market, which was valued at USD 107.04 billion in 2024, increased to USD 112.12 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach around USD 176.02 billion by 2034.
The Fuel Ethanol Market is significantly influenced by several critical factors, such as ened environmental awareness, governmental regulations, and the transition towards renewable energy alternatives. The increasing recognition of climate change has intensified efforts to minimize greenhouse gas emissions, with ethanol serving as a viable solution when used in conjunction with gasoline. Moreover, supportive government initiatives and incentives—like the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) in the United States and various international biofuel mandates—play a vital role in bolstering the production and use of ethanol. Technological advancements have also enhanced the efficiency of ethanol production from a variety of feedstocks, rendering it a more cost-effective option. Additionally, varying fossil fuel prices have a significant impact, as surges in oil costs often prompt both consumers and producers to explore alternative fuels such as ethanol. Finally, the increasing focus on sustainable farming practices further supports the growth of the fuel ethanol sector by encouraging the utilization of locally produced biofuels.
Fuel Ethanol Market Definition
Ethanol, a renewable form of alcohol extracted from various plant sources, is primarily utilized as an energy component in gasoline mixtures. It plays a significant role in lowering greenhouse gas emissions and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Ethanol as a fuel is important for its role in lowering greenhouse gas emissions, which aids in combating climate change. This renewable biofuel can be sourced from different types of biomass, such as corn and sugarcane, helping to enhance energy security while decreasing dependence on fossil fuels. Furthermore, ethanol increases the octane level of gasoline, leading to better engine efficiency. Its incorporation into gasoline blends is instrumental in advancing the shift towards more sustainable energy practices. Additionally, the cultivation and utilization of fuel ethanol support local economies and generate agricultural employment, positioning it as a crucial element in strategies for environmental sustainability and economic growth.
Fuel Ethanol Market Segmental Analysis:

Insights On Product
Sugar Based
The sugar-based category is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Ethanol Market. This is mainly attributed to the efficient conversion of sugarcane, beet, and other sugar crops into ethanol, providing a higher yield compared to starch-based and cellulosic sources. Countries like Brazil have demonstrated this efficiency, significantly boosting their ethanol production through sugar-based feedstocks, leading to lower production costs. The ongoing technological advancements in fermentation processes and an increasing focus on renewable energy sources contribute to further expansion in this area. Additionally, government policies supporting biofuels and sustainability are steering economies towards sugar-based ethanol, which is perceived as a more viable and immediate resource in many regions.
Starch Based
Starch-based ethanol production, primarily derived from corn and other cereal grains, has been a historically predominant player in the fuel ethanol market. While it continues to have a significant share, the growth potential is somewhat limited due to concerns over food versus fuel debates and the environmental impact of agricultural practices. However, the advancements in agricultural technology and the adoption of genetically modified crops have improved the efficiency and yield of starch-based ethanol, providing a slightly more competitive edge. Moreover, it plays a critical role in countries such as the United States, where it feeds into policies incentivizing local production for energy independence.
Cellulosic
Cellulosic ethanol presents a promising yet less dominant position in the fuel ethanol landscape. It is derived from lignocellulosic biomass—such as agricultural residues, wood chips, and non-food crops. While this method has great potential for sustainability and offers an innovative solution to the food versus fuel dilemma, the technology required for efficient production remains in the developmental phase. High production costs and challenges in breaking down the complex cellulose structure have hindered widespread adoption. Nevertheless, ongoing research is expected to enhance the viability of cellulosic ethanol in the future, aligning it more closely with sustainability goals set by governments worldwide.
Insights On Source
Natural
The Natural source of fuel ethanol is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Ethanol Market due to several factors. Firstly, there is a growing consumer preference for renewable and sustainable energy sources amid increasing environmental concerns. Natural fuel ethanol is derived from biomass and agricultural feedstocks, making it a more sustainable option compared to synthetic sources. Additionally, governments worldwide are implementing stringent regulations promoting the use of biofuels, leading to higher production and consumption of natural ethanol. The advancements in technology and techniques that enhance the efficiency of biofuel production further strengthen the position of natural fuel ethanol in the market.
Synthetic
Synthetic fuel ethanol is manufactured through chemical processes, typically using petroleum-derived feedstocks. Despite having applications in various industries, this is expected to lag behind due to a lack of sustainability compared to natural sources. Growing environmental awareness and the shift towards renewable energy have made synthetic ethanol less appealing to consumers. Moreover, the fluctuating prices of petroleum and the geopolitical tensions affecting oil supplies can further challenge this, making it less viable in the long run.
Insights On Raw Material
Sugarcane
Sugarcane is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Ethanol Market due to its high sugar content, which allows for efficient fermentation processes compared to other raw materials. It boasts a strong yield per hectare, making it economically viable for large-scale ethanol production. Countries like Brazil have established extensive sugarcane industries geared toward ethanol, leading to advanced production techniques and infrastructure. Furthermore, with the growing demand for renewable energy sources and stricter fuel regulations, sugarcane stands out as a leading option providing green energy alternatives. Its established agricultural practices and economic support render it a robust contributor to the fuel ethanol market.
Maize
Maize, also known as corn, plays a significant role in the fuel ethanol market, particularly in regions like the United States, where it is a major feedstock. The high starch content in maize makes it highly fermentable, which allows for efficient ethanol production. Additionally, the existing infrastructure for maize cultivation, coupled with government subsidies in favor of corn-based ethanol, enhances its attractiveness. However, fluctuating crop yields due to weather conditions can impact production levels.
Wheat
Wheat serves as an essential raw material for fuel ethanol, mainly in regions where maize is less dominant. Its starch content allows for the production of ethanol, although the efficiency is slightly less compared to maize. Wheat serves as a valuable alternative in parts of Europe, where it is widely cultivated. Additionally, the versatility of wheat as a food source means that there are established markets that can absorb excess supply, allowing producers to pivot towards ethanol production when necessary.
Industrial Beets
Industrial beets, particularly sugar beets, are notable for their dual-use in both sugar and fuel ethanol production. Though not as widely adopted as sugarcane or maize, they serve as a promising feedstock in regions like Europe and certain parts of North America. Their ability to yield high sugar content and grow in diverse climates makes them viable contenders. However, the market remains limited due to the more entrenched positions of other raw materials like maize and sugarcane.
Cereal And Starch
Cereal grains and starch crops like barley and rye contribute to the fuel ethanol market on a smaller scale. These crops can be fermented to produce ethanol; however, they are not the primary choice mainly due to lower yield efficiencies compared to maize and sugarcane. Nonetheless, with advancements in technology, there is potential for increasing their utilization and exploring niche applications.
Other Raw Materials
This category encompasses various unconventional feedstocks such as waste biomass, cassava, and various fruits. While their contribution to the fuel ethanol market remains minor compared to the dominant materials, research is ongoing to optimize their use. The benefit of utilizing waste feedstocks aligns with sustainability objectives, potentially paving the way for their increased adoption in future fuel ethanol production.
Insights On Application
Flexible Fuel Vehicles
The Flexible Fuel Vehicles (FFVs) category is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Ethanol Market due to its inherent flexibility in utilizing various blends of ethanol and gasoline. FFVs can operate on fuels with varying ethanol content, which appeals to both consumers and manufacturers as it supports the transition towards renewable energy sources. Moreover, the rising global awareness regarding environmental sustainability and government initiatives promoting cleaner fuels further boost the demand for such vehicles. With increasing investments in biofuel infrastructure and incentives for consumers to adopt greener vehicles, the flexibility offered by these vehicles aligns well with market trends, thereby positioning FFVs as the leading sector in the fuel ethanol market.
Conventional Vehicles
Conventional Vehicles represent a significant in the Global Fuel Ethanol Market, particularly in regions where traditional gasoline engines are still prevalent. These vehicles primarily rely on gasoline, but their compatibility with low ethanol blends allows for market penetration of fuel ethanol. However, due to less flexibility compared to FFVs, the growth potential for this vehicle type is somewhat limited, as the industry shifts towards more advanced technologies and renewable fuel options. Despite these challenges, conventional vehicles continue to play a role as a transitional element in the adoption of ethanol blends, especially in markets where infrastructure for FFVs might not be fully developed.
Flexible Fuel Vehicles
Flexible Fuel Vehicles (FFVs) stand out in the Global Fuel Ethanol Market due to their ability to run on a mix of ethanol and gasoline. This adaptability not only caters to consumer preferences for renewable energy sources but also aligns with regulatory efforts aimed at reducing carbon emissions. The increasing availability of ethanol fuel at various gas stations and government incentives for using cleaner fuels further drive the adoption of FFVs. However, compared to conventional vehicles, they require substantial initial investment in infrastructure and consumer education to maximize their potential. As awareness grows, FFVs are likely to witness increased penetration in the market, offering a crucial alternative for environmentally-conscious consumers.
Insights On End-User
Automotive
The automotive sector is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Ethanol Market due to the rising demand for cleaner fuel alternatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and comply with stringent environmental regulations. E85 and other ethanol-blended fuels are gaining popularity as automobile manufacturers increasingly focus on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints. Government incentives, such as tax credits and renewable fuel standards, further drive the adoption of ethanol in vehicles. Additionally, the growing popularity of flex-fuel vehicles, engineered to run on high-ethanol blends, exemplifies the sector’s strong growth trajectory. The automotive industry's transition toward electric vehicles and biofuels positions ethanol as a crucial alternative, making it the leading user in the market.
Oil And Gas
The oil and gas industry plays a vital role in the fuel ethanol market, primarily through the blending of ethanol with gasoline to enhance octane levels and reduce vehicle emissions. Oil refineries utilize ethanol to meet regulatory requirements for renewable fuel standards, which mandates a certain percentage of biofuels in traditional fossil fuels. Furthermore, as companies strive to differentiate themselves and improve sustainability metrics, investments in ethanol processing and infrastructure are increasingly prevalent. Nevertheless, the industry's growth is hindered by lower oil prices, which can make gasoline more economical compared to ethanol blends. Despite these challenges, the demand for cleaner fuel solutions continues to support the oil and gas industry's involvement in the ethanol marketplace.
Other End Users
The "Other End Users" category accounts for diverse industries utilizing fuel ethanol, including industrial processes, food and beverage production, and chemical manufacturing. This 's growth is primarily driven by ethanol's multifunctional properties, such as serving as a solvent or an antibacterial agent. Additionally, ethanol is increasingly being utilized in the production of renewable chemicals and bioplastics. However, the share of this category is relatively smaller compared to automotive and oil and gas uses because these end users typically do not drive large-scale consumption like the automotive sector. As a result, while there are opportunities in niche applications, this is less prominent than the leading sectors.
Global Fuel Ethanol Market Regional Insights:
North America
North America is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Ethanol market due to several factors, including established agricultural practices, a robust biofuel policy framework, and advanced technology in production processes. The U.S. and Canada's significant investments in renewable energy and governmental incentives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have fostered a favorable environment for the growth of ethanol production. Additionally, the vast availability of feedstocks such as corn and sugarcane in the U.S. allows for greater efficiency and lower production costs. The region also benefits from a mature infrastructure for blending and distributing fuel ethanol, further positioning it as the leading area in the global market.
Latin America
In Latin America, Brazil is a key player in the fuel ethanol market, known for its pioneering role in biofuels since the 1970s. The nation boasts large sugarcane plantations and a well-developed infrastructure for ethanol production and distribution. Strong governmental support, particularly in renewable fuel mandates, promotes ethanol use in the transportation sector. However, challenges related to feedstock competition with food production and environmental issues can hinder growth. Despite this, Brazil's established market makes Latin America a significant part, but it remains behind North America in overall dominance.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region is witnessing increased growth in the fuel ethanol market, driven mainly by nations like India and Australia. India's government has introduced policies to incorporate ethanol blending in gasoline to improve energy security and reduce pollution. However, production capacity and reliance on imports remain challenges for the region. While advancements in technology and an urgent need for cleaner fuels provide growth opportunities, the availability of feedstocks and the economic feasibility of production are critical factors that could impact progress.
Europe
Europe is focusing on sustainable energy, with regulations driving the demand for fuel ethanol. The European Union has set ambitious targets for renewable energy, leading to increased interest in ethanol as a cleaner alternative. Key markets like Germany and France engage in blending ethanol with gasoline. However, the competition for feedstocks with the food industry and fluctuating policies may limit its growth compared to North America. Therefore, while Europe is making strides in the sector, it does not lead in overall market dominance.
Middle East & Africa
In the Middle East and Africa, growth in the fuel ethanol market faces several obstacles, including limited agricultural infrastructure and economic instability. Countries like South Africa show potential due to ongoing initiatives to use biofuels as part of sustainable energy goals. However, the region still lags significantly compared to more developed markets like North America and Europe. Reliance on fossil fuels and a lack of substantial investment in renewable technologies hinder the progress of fuel ethanol adoption. Thus, while the region is attempting to develop, it remains a minor player in the global market.
Fuel Ethanol Competitive Landscape:
The primary participants in the international fuel ethanol sector include leading manufacturers and distributors who enhance production efficiency through innovative technologies. These entities also play a significant role in shaping market dynamics through strategic collaborations and sustainability efforts. Their contributions are vital for modifying supply chains and complying with regulatory requirements, thereby promoting the use of biofuels.
The fuel ethanol sector is primarily driven by several major companies, including Archer Daniels Midland Company, POET LLC, Green Plains Inc., Valero Energy Corporation, and Pacific Ethanol Inc. Other important players in the industry are The Andersons Inc., Flotek Industries, Inc., CropEnergies AG, Cosan Limited, and Raízen S.A. from Brazil. Additionally, firms like Al-Corn Clean Fuel, Cargill Inc., BioEnergy International GmbH, Abengoa Bioenergy, and Rex American Resources Corporation contribute significantly to the market. Furthermore, notable enterprises such as Mailto Norseman, ICM Inc., Sweetwater Energy, GranBio, and Lallemand Inc. are essential in the production and distribution of fuel ethanol on a global scale, fostering progress in the renewable energy landscape.
Global Fuel Ethanol COVID-19 Impact and Market Status:
The Covid-19 pandemic caused substantial upheaval in the worldwide fuel ethanol sector, as lockdown measures and the transition to remote working drastically diminished fuel consumption. This decline in demand subsequently led to lower production levels and posed financial difficulties for the industry.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound effect on the fuel ethanol sector, primarily driven by reduced transportation activity and economic downturns, which resulted in a notable fall in gasoline consumption. With the implementation of stay-at-home orders and lockdown measures, the use of ethanol-blended fuels saw a significant reduction, forcing many ethanol production facilities to either halt operations or cut back on their output. This disruption, combined with a sharp decline in oil prices, exerted additional downward pressure on ethanol pricing, jeopardizing the financial stability of numerous producers. Nonetheless, the pandemic also ignited a renewed interest in biofuels as part of the recovery strategies targeting greener energy solutions. Governments and industries began to prioritize sustainability, leading to initiatives aimed at revitalizing the ethanol market in the aftermath of the pandemic. As restrictions gradually ease and travel and transportation activities resume, a recovery in the fuel ethanol industry is expected, fostering innovation and responsiveness to evolving market conditions, including a greater incorporation of renewable energy sources within the fuel mix.
Latest Trends and Innovation in The Global Fuel Ethanol Market:
- In October 2023, Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM) announced the completion of its acquisition of a majority stake in the biorefinery operations of East Kansas Agri-Energy, significantly expanding its ethanol production capacity and reinforcing its commitment to sustainable fuel sources.
- In September 2023, POET LLC unveiled its latest technology innovation, a new enzyme blend that improves the efficiency of ethanol production by 10%, enabling lower production costs and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- In August 2023, Green Plains Inc. entered into a joint venture with the agricultural bioproducts company, BioProcess Algae, to develop integrated biorefinery systems aimed at utilizing carbon capture technology in ethanol production.
- In July 2023, Pacific Ethanol, Inc. announced the finalization of its merger with Al-Corn Clean Fuels, creating one of the largest independent ethanol producers in the U.S. to enhance market competitiveness and expand geographic reach.
- In June 2023, Valero Energy Corporation expanded its ethanol production facility in Mount Pleasant, Texas, investing an estimated $150 million in advanced technology to increase yield and efficiency while reducing operational costs.
- In May 2023, the Renewable Fuels Association (RFA) launched an initiative to promote the use of higher blends of ethanol in gasoline, collaborating with major oil companies and automakers to increase market uptake.
- In April 2023, Flint Hills Resources announced that it successfully completed a significant upgrade at its ethanol plant in Fairmont, Minnesota, which included the implementation of advanced fermentation technologies to boost production rates by 15%.
- In March 2023, Monarch Bioenergy, a joint venture between the renewable energy firm Biodico and the agricultural company Outland Renewable Energy, unveiled a new facility dedicated to producing cellulosic ethanol from agricultural waste, emphasizing sustainability in the fuel ethanol sector.
- In February 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finalized a rule that allows a temporary increase in the volume of ethanol blending, prompting companies like DuPont to accelerate research on advanced ethanol production technologies.
- In January 2023, Green Plains Partners LP completed an acquisition of an additional six ethanol storage facilities, further enhancing its logistics capabilities and operational efficiencies for fuel-grade ethanol distribution.
Fuel Ethanol Market Growth Factors:
The growth of the fuel ethanol sector is propelled by a rising need for renewable energy alternatives, strict governmental policies aimed at reducing emissions, and innovations in production methods.
The fuel ethanol market is experiencing significant expansion due to a combination of factors that include a rising need for renewable energy and increasingly stringent environmental regulations aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions. As global concerns about climate change and air quality intensify, governments around the world are enacting policies that favor biofuels like ethanol as viable alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. Innovations in production methods, such as advanced fermentation processes and the incorporation of cellulosic materials, have further optimized ethanol production, resulting in higher yields and decreased costs, which enhance its market competitiveness. Additionally, the automotive sector is shifting towards flexible-fuel vehicles capable of accommodating higher ethanol blends, fostering further growth in the market. The volatility of oil prices and the pursuit of energy independence also drive nations to diversify their energy portfolios, leading to an increase in domestic ethanol production. Consumer awareness regarding the advantages of renewable energy sources is growing, alongside improvements in the infrastructure necessary for blending and distribution, thereby bolstering market development. Lastly, international trade agreements that ease the exchange of biofuels enhance the interconnectedness and dynamism of the fuel ethanol market on a global scale.
Fuel Ethanol Market Restaining Factors:
The market for fuel ethanol is confronted with substantial obstacles due to variable costs of raw materials, strict regulatory frameworks, and rivalry with other forms of energy.
The Fuel Ethanol Market encounters a range of constraints that could impede its expansion. Significant challenges stem from the volatility of feedstock prices, notably for corn and sugarcane, which have a direct influence on production expenses and overall profitability. Moreover, the sector faces stiff competition from alternative renewable energy sources like biodiesel and electric vehicles, which necessitate that fuel ethanol demonstrate its practicality and long-term viability. Regulatory hurdles and fluctuating government policies surrounding biofuels may further muddle market conditions, instilling uncertainty among stakeholders. Environmental issues, particularly those related to land use changes and the greenhouse gas emissions linked to ethanol production, also fuel doubts about its sustainability. In addition, current technological constraints in production processes might limit the efficiency and scalability of ethanol manufacturing, thereby affecting its competitiveness against fossil fuels. Nevertheless, continuous technological advancements, rising consumer appetite for cleaner energy options, and supportive policies aimed at renewable energy could create pathways for innovation and market growth in the fuel ethanol industry. As the focus increasingly shifts towards sustainability and environmental accountability, the market is poised to adapt and grow, potentially enhancing participation and dynamics in the upcoming years.
Key Segments of the Fuel Ethanol Market
By Product
- Starch Based
- Sugar Based
- Cellulosic
By Source
- Synthetic
- Natural
By Raw Material
- Maize
- Wheat
- Industrial Beets
- Sugarcane
- Cereal And Starch
- Other Raw Materials
By Application
- Conventional Vehicles
- Flexible Fuel Vehicles
By End-User
- Automotive
- Oil And Gas
- Other End Users
Regional Overview
North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of Middle East and Africa
Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America

