Enterprise Asset Leasing Market Analysis and Insights:
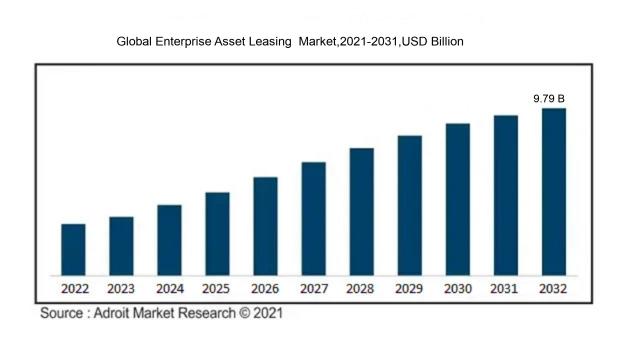
In 2023, the size of the worldwide Enterprise Asset Leasing market was US$ 4.75 billion. Adroit Market Research projects that the market will increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.9% from 2024 to 2032, reaching US$ 9.79 billion.
The Enterprise Asset Leasing Market is fundamentally influenced by several critical factors. Primarily, the necessity for companies to optimize capital management prompts them to consider leasing assets instead of purchasing them outright, which helps maintain healthy cash flow. Furthermore, the growing intricacies and expenses associated with asset ownership lead businesses to prefer leasing arrangements that provide both flexibility and scalability. The swift pace of technological innovation requires organizations to update their equipment regularly; leasing enables them to remain competitive while avoiding steep depreciation costs. Additionally, the ongoing trend of digital transformation and the pursuit of improved operational efficiency fuel the demand for leasing, as businesses aim to utilize cutting-edge technology without incurring substantial financial strain. Furthermore, the advantageous tax implications of lease payments in comparison to ownership, along with the appealing financing options offered by lessors, significantly bolster market growth. As companies respond to changing economic dynamics, the inclination towards asset leasing is anticipated to accelerate, solidifying its position as a vital financial strategy.
Enterprise Asset Leasing Market Definition
Enterprise Asset Leasing involves the procurement and utilization of assets, such as machinery or equipment, via leasing arrangements instead of outright purchases. This strategy enables organizations to optimize cash flow management while gaining access to essential resources without the need for an initial capital expenditure.
Enterprise Asset Leasing plays a vital role in allowing companies to obtain necessary equipment and technology while circumventing the significant initial expenses tied to outright purchases. This financial strategy enhances cash flow, empowering organizations to invest in growth and innovation instead of merely acquiring assets. Furthermore, leasing introduces flexibility, permitting businesses to transition to more advanced equipment as their requirements change. It may also provide advantageous tax implications and mitigate the risks linked to asset depreciation. In summary, enterprise asset leasing is a strategic financial choice that bolsters operational efficiency and strengthens competitive positioning in dynamic market environments.
Enterprise Asset Leasing Market Segmental Analysis:

Insights On Asset Type
Movable Assets
Movable assets are poised to dominate the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing Market due to their high demand in various industries such as construction, transportation, and manufacturing. This category encompasses equipment, vehicles, and machinery, which are essential for operational efficiency and can often be leased instead of purchased outright. The flexibility that leasing offers businesses, particularly in managing cash flow and capital expenditures, reinforces the appeal of movable assets. As companies aim to remain agile and reduce capital risk, the trend toward leasing movable assets over outright ownership is expected to grow, making this the leading force in the enterprise asset leasing landscape.
Immovable Assets
Immovable assets, including real estate and infrastructure, serve as a critical component of enterprise asset leasing. Businesses frequently require these assets for operational bases, which can directly impact their growth and expansion strategies. However, leasing immovable assets often involves longer-term commitments and higher initial costs compared to movable assets. The complexities surrounding property management, regulatory considerations, and the slow pace of real estate transactions further position immovable assets in a different category, where they may not achieve the rapid growth seen with movable assets in the leasing market.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets, such as software and patents, represent an increasingly important part of the asset leasing market. As businesses embrace digital transformation and reliance on technology escalates, the demand for leasing these assets is anticipated to grow. However, compared to movable assets, the market for intangible assets remains less mature and less understood, which could stymie the potential for rapid dominance. Moreover, issues surrounding intellectual property rights and valuation can complicate leasing agreements, making the leasing of intangible assets a more niche activity rather than a driving force in the enterprise asset leasing market.
Insights On Industry Verticals
IT and Telecommunications
The IT and Telecommunications sector is expected to dominate the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing Market due to its rapid technological advancements and increasing investment in infrastructure. This industry demands flexibility and agility in asset management as companies seek to maximize operational efficiency while minimizing capital expenditure. The rising adoption of cloud computing, software-as-a-service (SaaS), and big data analytics also compel firms to lease rather than purchase assets outright, allowing them to stay ahead in a competitive market. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on digital transformation initiatives across businesses underpins the need for flexible leasing solutions, further propelling this sector to the forefront of the market.
Manufacturing
The Manufacturing sector is significantly influenced by asset leasing as companies strive to modernize and innovate their production processes. Leasing enables manufacturers to acquire technologically advanced machinery without the substantial upfront costs associated with purchases. This model allows firms to maintain operational efficiency while managing cash flows effectively. As sustainability becomes a priority, many manufacturers are also looking to lease equipment that helps reduce environmental impact, making this market increasingly relevant.
Healthcare
In the Healthcare sector, asset leasing is crucial as it allows facilities to access state-of-the-art medical equipment without incurring high capital expenditures. This industry often faces stringent budgeting and cost-control measures, making leasing an attractive option to maintain high standards of care without compromising financial stability. As telemedicine and digital health solutions continue to proliferate, leasing options that support modern medical technologies are gaining traction, aligning with healthcare providers' needs for flexibility and scalability.
Transportation and Logistics
The Transportation and Logistics sector is characterized by the necessity to keep pace with ever-changing market demands. Asset leasing offers companies the chance to upgrade their fleets and logistics equipment frequently, ensuring they remain competitive. This flexibility is crucial in an industry where operational efficiency directly impacts profits. Additionally, companies are focused on sustainability and fuel efficiency, prompting greater interest in leasing solutions that enable access to environmentally friendly vehicles and technologies.
Energy and Utilities
The Energy and Utilities sector is gradually embracing asset leasing as a means to finance new technologies and infrastructure upgrades without heavy capital investments. Companies in this field face the dual pressures of regulatory compliance and the need for modernization to support renewable energy initiatives. Leasing provides these firms with the flexibility required to adopt new technologies while managing economic risks effectively in a landscape marked by rapid change and innovation.
Government and Public Sector
In the Government and Public Sector, asset leasing helps agencies acquire necessary resources and technology while adhering to budgeting constraints. This sector often faces limitations on capital spending, making leasing an appealing alternative for funding essential projects and infrastructure. As governments focus on modernization and efficiency improvements, leasing models offer a means to access updated technologies without upfront costs, aligning with the fiscal responsibility expected from public entities.
Insights On Asset Lease Type
Operating Lease
Operating leases are expected to dominate the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing Market due to their flexibility and the growing preference for businesses to avoid large capital expenditures. This leasing type allows companies to use assets without needing to own them outright, which reduces financial risks associated with asset depreciation. Additionally, businesses across various sectors favor operating leases to maintain financial liquidity and manage assets more effectively, especially in rapidly changing markets. The increasing trend toward outsourcing and the necessity of cutting costs further reinforces the appeal of operating leases as businesses seek to align their asset utilization with their operational needs without tying up substantial capital.
Capital Lease
Capital leases, while less prevalent than operating leases, are characterized by the transfer of ownership benefits and risks associated with the asset. These leases are generally favored by businesses looking for long-term asset use and those desiring to capitalize on tax benefits. Companies often opt for capital leases when they project prolonged use of an asset, allowing them to amortize the asset over its useful life. However, since capital leases require more commitment and financial scrutiny, they may not appeal to businesses seeking flexibility, leading to a smaller share in the overall market compared to operating leases.
Sale and Leaseback
Sale and leaseback transactions enable companies to free up capital by selling their existing assets and leasing them back concurrently. This financial strategy is appealing to businesses needing cash for operational expenses or investments while retaining the use of critical assets. It provides a dual advantage: enhancing cash flow while keeping essential operational capabilities intact. However, this type lacks the flexibility most companies seek, often resulting in a smaller share of the market. Its reliance on infrastructure and real estate makes it suitable primarily for specific industries such as manufacturing and property management, which may limit its overall market presence compared to other leasing options.
Insights On Lease Term
Medium-term (3-5 years)
Medium-term leasing is expected to dominate the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing Market due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness for businesses. In a rapidly changing economic landscape, companies often prefer leasing arrangements that provide a balance between short-term adaptability and long-term commitment. Medium-term leases allow organizations to adapt to fluctuating market conditions and technological advancements without being locked into lengthy agreements. Additionally, this duration offers a favorable depreciation period for equipment and assets, making it appealing for enterprises that want to maximize operational efficiency while minimizing capital expenditures. The growing trend towards transitional and project-based work is also contributing to the rise of medium-term leasing arrangements.
Short-term (up to 3 years)
Short-term leasing arrangements cater to businesses looking for rapid access to assets without long-term financial commitments. This model is particularly appealing to startups or firms engaged in projects with a limited duration, as it enables agility and operational flexibility. Companies appreciate short-term leases for equipment or office space that can be quickly adjusted to meet immediate demands. However, while this approach facilitates fast-paced adaptability, it may not offer the best long-term value compared to more extended lease agreements, limiting its appeal in a broader context.
Long-term (over 5 years)
Long-term leases are characterized by stability and predictability, making them suitable for large enterprises that require consistent usage of assets over an extended period. Companies with established operations often prefer this option as it typically offers lower monthly payments and can lead to more favorable terms. Additionally, long-term leasing is advantageous for planning and budgeting, particularly for industries that depend on capital-intensive machinery. However, the growing need for flexibility in assets may limit its dominance as companies often seek arrangements that allow for quicker adjustments in their operational needs.
Insights On Lease Structure
Single-tenant Lease
The Single-tenant Lease is expected to dominate the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing Market. This lease structure provides companies with significant flexibility, allowing them to tailor lease terms to meet specific operational needs. Such customization often leads to greater income predictability for lessors because the arrangement minimizes the complexities associated with managing multiple tenants. Demand for specialized equipment in an increasingly competitive environment underscores the preference for single-tenant arrangements. Furthermore, these leases often appeal to larger corporations seeking dedicated facilities where they can leverage operational efficiencies, thus driving the market’s expansion in this domain.
Multi-tenant Lease
The Multi-tenant Lease structure presents a viable alternative for companies that prefer shared resources and reduced overhead costs. This model facilitates the ability for companies to occupy a portion of a larger asset, enabling them to share expenses associated with maintenance and management. It appeals particularly to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that might not commit to large spaces or incur heavy financial burdens. The adaptability to diverse business needs makes this arrangement popular, especially in urban areas where space is limited and expensive.
Sale-Leaseback
The Sale-Leaseback model offers unique financial advantages, enabling businesses to free up capital tied in their real estate while still maintaining operational control of the assets. This arrangement allows companies to sell their properties to investors and lease them back, thus generating immediate liquidity while retaining the use of essential facilities. It's increasingly favored by organizations looking to enhance cash flow and financial flexibility, particularly during economic uncertainties. The potential for tax benefits further solidifies its position as an attractive option within the asset leasing landscape.
Global Enterprise Asset Leasing Market Regional Insights:
North America
North America is expected to dominate the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing market primarily due to the presence of a highly developed financial sector, advanced technology adoption, and a stable regulatory environment. The United States, in particular, significantly contributes to this growth, with numerous players in the asset leasing space leveraging sophisticated leasing solutions to optimize operations. Additionally, an increase in businesses looking for flexible financing options and the rising trend of outsourcing non-core functions further bolster the market in this region. The competitive landscape, along with innovative leasing models and services, positions North America as the leader in this sector.
Latin America
Latin America is witnessing growth in the Enterprise Asset Leasing market, driven by evolving economic conditions and an increasing number of businesses seeking efficient asset management solutions. Countries like Brazil and Mexico are beginning to explore leasing options to optimize investments and manage cash flow more effectively. However, challenges such as economic volatility and regulatory uncertainties still pose significant threats to the expansion of this market in the region. As businesses gradually adopt leasing as a standard practice, there is potential for growth, though it may not dominate in the near future.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region is a burgeoning market for Enterprise Asset Leasing, propelled by rapid economic growth, urbanization, and a rise in corporate financing needs. Countries like China and India are becoming players, as businesses increasingly seek flexible asset management options. The demand for leasing is likely to rise due to investments in various sectors, including technology and telecommunication. However, the region faces challenges regarding regulatory frameworks and infrastructure limitations that may hinder growth. Despite these obstacles, the area's large population and rising middle class present opportunities for market expansion in the future.
Europe
Europe is a strong contender in the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing market, driven by a mature economy, established financial institutions, and a high level of regulatory compliance. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are leading the charge, with businesses actively seeking leasing solutions to enhance their operational efficiency. The increasing focus on sustainability has also propelled interest in leasing assets rather than purchasing them outright. However, the region is experiencing fluctuations due to economic uncertainties and varying regulatory requirements across countries, posing challenges to consistent growth in the market.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region is gradually positioning itself within the Enterprise Asset Leasing market, thanks to ongoing economic diversification efforts and substantial investments in infrastructure. Countries in the Gulf Cooperation Council, like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, are seeing increased interest from businesses in leasing assets to manage costs and improve liquidity. Despite this, the region grapples with geopolitical risks and fluctuating oil prices, which can affect market stability. As more companies recognize the benefits of asset leasing, there is potential for growth, although it remains limited compared to other regions.
Enterprise Asset Leasing Market Competitive Landscape:
Major contributors within the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing sector play a crucial role in delivering financial solutions along with adaptable leasing alternatives, enabling companies to enhance their asset use. Their creative leasing frameworks and funding approaches stimulate market expansion and increase access to vital equipment and technology.
The principal entities in the Enterprise Asset Leasing sector consist of Wells Fargo, GE Capital, IBM, Siemens Financial Services, DLL Group, Caterpillar Financial Services, Hitachi Capital America, CIT Group, Arvig Enterprises, and Ivory Consulting Corporation. Other significant firms include Amex Global Business Travel, Element Fleet Management, Matsui & Co., Inc., TCF Equipment Finance, Marlin Business Services, and Finova Financial. Furthermore, organizations such as SunTrust Equipment Finance & Leasing Corp, U.S. Bank Equipment Finance, and LeasePlan also have considerable influence in the market.
Global Enterprise Asset Leasing Market COVID-19 Impact and Market Status:
The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly impacted the Global Enterprise Asset Leasing sector, leading to a decrease in the demand for leased assets as a result of economic instability and the suspension of operations in numerous industries.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound effect on the Enterprise Asset Leasing sector, resulting in a more conservative investment approach where companies prioritized liquidity and the stability of operations over significant capital expenditures. Amid economic volatility, many enterprises postponed new lease agreements and concentrated on extending current leases, leading to a reduction in new leasing activities. Industries such as transportation and manufacturing, which are heavily dependent on leased assets, witnessed considerable downturns, whereas sectors like technology experienced ened demand for cloud services and leasing of equipment as remote work became prevalent. Moreover, the pandemic hastened the process of digital transformation and spurred the adoption of flexible leasing frameworks, as organizations aimed to enhance asset efficiency and maintain agility in unpredictable circumstances. As a result, although the leasing market encountered obstacles, it also fostered innovation and a transition towards leasing strategies that are more resilient and adaptable, capable of responding to the evolving needs of the market in the post-pandemic era.
Latest Trends and Innovation in The Global Enterprise Asset Leasing Market:
- In September 2023, Caterpillar Financial Services Corporation announced the acquisition of a major equipment leasing firm, helping to expand its portfolio and enhance service offerings for construction and mining industries.
- In August 2023, JLL (Jones Lang LaSalle) unveiled a new technology platform called Smart Asset Management, utilizing artificial intelligence to optimize asset utilization and financial forecasting for enterprise clients.
- In July 2023, GE Capital announced the launch of a blockchain-based solution aimed at improving the asset leasing process, enhancing transparency and reducing transaction times across industries.
- In May 2023, DLL Group, a global vendor financing company, expanded its services in the renewable energy sector by merging with a leading solar leasing company, reinforcing its commitment to sustainable energy solutions.
- In April 2023, Equipment Leasing and Finance Association (ELFA) hosted its annual conference, where industry leaders discussed innovations in technology-driven asset management and financing solutions.
- In March 2023, Siemens Financial Services completed its strategic partnership with an emerging fintech company to design advanced leasing options specifically for digital and electric vehicle technologies.
- In February 2023, Volvo Financial Services launched a new program called Flexi Lease, allowing flexible leasing terms for customers acquiring electric and hybrid vehicles, thereby promoting greener transportation solutions.
- In January 2023, IBM announced its entry into the asset leasing market with a new AI-powered leasing management system, simplifying lease administration and enhancing efficiency for enterprise clients.
- In December 2022, Verizon announced the successful acquisition of a tech startup specializing in IoT asset tracking solutions, aimed at integrating advanced tracking capabilities into its leasing operations for better asset visibility.
Enterprise Asset Leasing Market Growth Factors:
The expansion of the Enterprise Asset Leasing Market is fueled by a rising need for budget-friendly asset management strategies and a commitment to improving operational effectiveness across multiple industries.
The Enterprise Asset Leasing sector is experiencing notable expansion, influenced by several pivotal elements. Primarily, the increasing emphasis on cost management has prompted organizations to transition from capital expenditures to operational expenditures, rendering leasing a more favorable alternative. This shift is augmented by technological advancements that optimize asset management and facilitate seamless leasing procedures.
Moreover, the ened commitment to sustainability and the circular economy drives companies to opt for leasing over purchasing, thereby enhancing resource efficiency. The rapid growth of industries such as healthcare, construction, and manufacturing further intensifies the demand for specialized assets that may entail high acquisition costs.
In addition, attractive financing solutions and the rise of adaptable leasing structures make it easier for startups and small to medium-sized enterprises to access essential equipment without hefty initial outlays. The globalization of markets also allows firms to utilize assets across different regions more effectively, boosting their operational potential.
Finally, supportive regulations and tax benefits related to equipment leasing highlight its financial soundness, reinforcing its appeal as a strategy for asset management. Collectively, these factors are driving a strong growth trajectory for the Enterprise Asset Leasing Market, setting it up for continued development in the future.
Enterprise Asset Leasing Market Restaining Factors:
Critical limiting factors in the Enterprise Asset Leasing Market encompass economic instability, rigorous regulatory standards, and the possibility of variable interest rates.
The Enterprise Asset Leasing sector encounters a variety of constraints that could hinder its expansion. One major hurdle is the variability of interest rates, which can alter the overall expenses associated with leasing agreements, potentially dissuading firms from committing to long-term leases. Moreover, the escalating intricacy of financial regulations and compliance demands can pose obstacles for businesses evaluating asset leasing options, leading to ened operational expenses and uncertainty. Additionally, there is a rising trend among corporations favoring direct purchases rather than leasing arrangements, especially in a rapidly evolving technological landscape, where the prospect of leased assets becoming outdated makes long-term commitments less attractive. The substantial upfront capital required to develop leasing infrastructures can also deter smaller enterprises from participating in the market. Despite these obstacles, the Enterprise Asset Leasing sector presents opportunities for growth, propelled by technological innovations that improve asset management and operational efficiency. As organizations increasingly acknowledge the advantages of flexibility and access to modern equipment without significant financial investments, the market is likely to evolve and innovate, thus creating a more dynamic leasing environment.
Segments of the Enterprise Asset Leasing Market
By Asset Type
• Movable Assets
• Immovable Assets
• Intangible Assets
By Industry Verticals
• Manufacturing
• Healthcare
• IT and Telecommunications
• Transportation and Logistics
• Energy and Utilities
• Government and Public Sector
By Asset Lease Type
• Capital Lease
• Operating Lease
• Sale and Leaseback
By Lease Term
• Short-term (up to 3 years)
• Medium-term (3-5 years)
• Long-term (over 5 years)
By Lease Structure
• Single-tenant Lease
• Multi-tenant Lease
• Sale-Leaseback
Regional Overview
North America
• US
• Canada
• Mexico
Europe
• Germany
• France
• U.K
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• Japan
• India
• Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
• Saudi Arabia
• UAE
• Rest of Middle East and Africa
Latin America
• Brazil
• Argentina
• Rest of Latin America

